Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio . The different levels limit which. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. there are four main levels of measurement: Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius.
from kidspressmagazine.com
temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. The different levels limit which. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius.
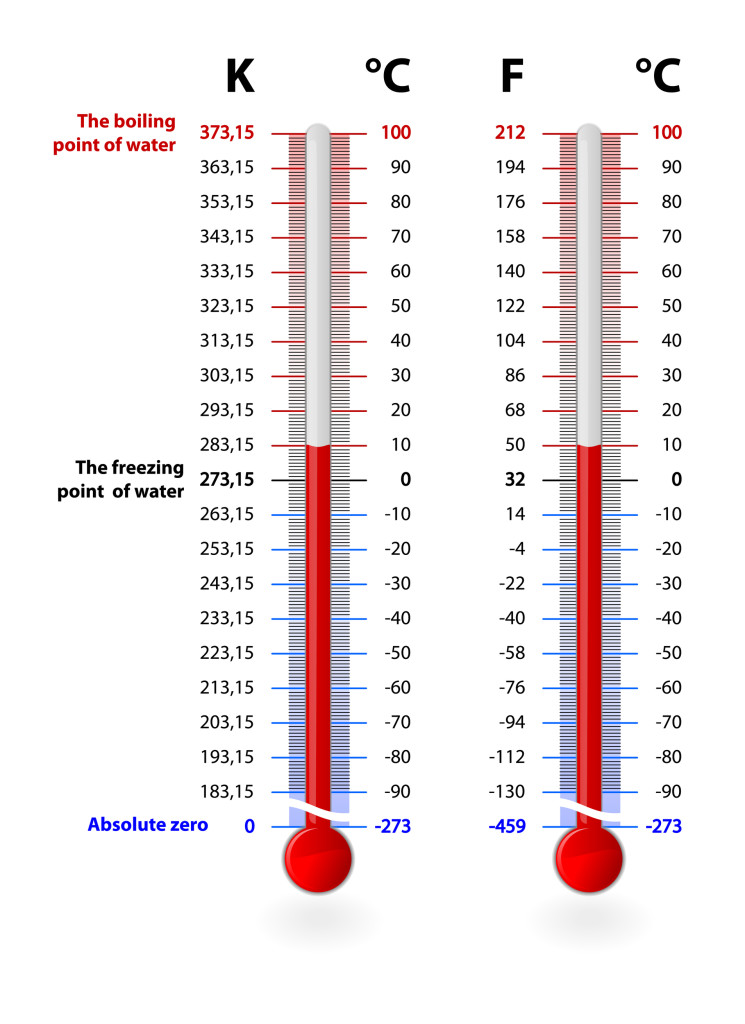
Temperature Scales Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin
Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. The different levels limit which. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have.
From www.numerade.com
Variable Type of variable Level of measurement Quantitative Nominal Ordinal Interval Categorical Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.mymarketresearchmethods.com
Types of data measurement scales nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. temperature scales like celsius (c). Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED For each of the variables described below indicate whether it is quantitative or Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: The different levels limit which. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Level of Variable Type of variable measurement Nominal Ordinal Quantitative (a Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED For each of the variables described below indicate whether it is quantitative or Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From learningschoolmiszegzy.z22.web.core.windows.net
Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Examples Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. The different levels limit which. there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Which measurement scale represents numerical variable? Ordinal Interval Nominal Question Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency.. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.scribbr.co.uk
What Is Ratio Data? Examples & Definition Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. . Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From theintactone.com
Level of Measurement Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, and Ratio Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. there are four main levels of measurement: within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From slideplayer.com
Definition & Measurement ppt download Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. there are four main levels of measurement: Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. The different levels limit which. . Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From gradcoach.com
Nominal, Ordinal, Interval & Ratio Explained Simply Grad Coach Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: The different. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From international.rujukannews.com
Scales of Measurement Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale Data Rujukan International Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. there are four main levels of measurement: In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. The different levels limit which. . Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Question 5 082 Room temperature (Fahrenheit) Incorrect Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio A Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From gann-dee.blogspot.com
Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio PPT Math 2260 Introduction to Probability and Statistics Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio The different levels limit which. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in degrees celsius. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. there are four main levels of measurement: . Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From mavink.com
What Is Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. In this guide, we’ll explain exactly what is meant by levels (also known as. temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED For each of the variables described below, indicate whether it is a quantitative or Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: The different levels limit which. there are four main levels of measurement: the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. . Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From brainly.com
For each of the variables described below, indicate whether it is a quantitative or a Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio interval variables are variables for which their central characteristic is that they can be measured along a continuum and they have. within each of these two main categories, there are two levels of measurement: temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.
From mavink.com
Types Of Data Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio this allows you to measure standard deviation and central tendency. there are four main levels of measurement: temperature scales like celsius (c) and fahrenheit (f) are measured by using the interval scale. the level at which you measure a variable determines how you can analyze your data. Everyone's favorite example of interval data is temperatures in. Temperature (In Degrees Fahrenheit) Quantitative Categorical Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio.